EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM IN THE US
PRIMARY EDUCATION
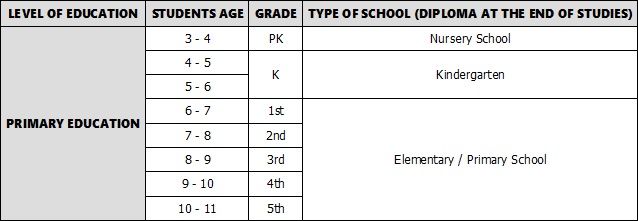
American students generally start their education in Kindergarten at the age of 4. They may also go to Nursery School from 3 to 4 years old if their parents wish. Children attend 2 years of Kindergarten before enrolling in an Elementary School, also called primary school. They then start what is referred to First Grade and will follow courses there until Fifth Grade, so until 11 years old, and then their primary education is completed.
SECONDARY EDUCATION
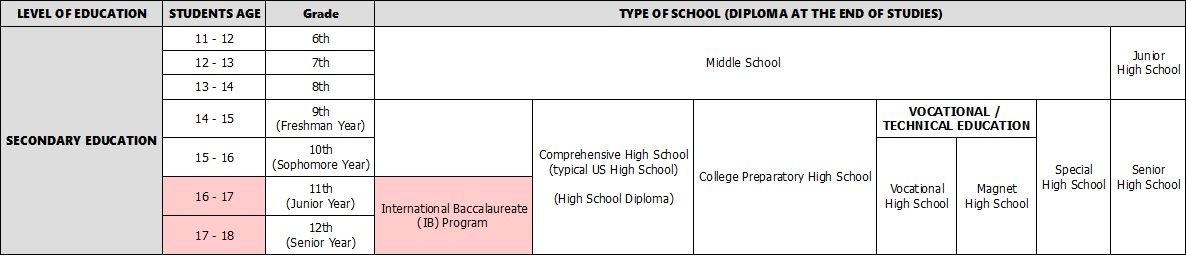
Students attend Grades 6 through 8 in a Middle School or Junior High School. Middle schools and Junior High schools differ in the following: Middle schools are more student-oriented and the education they provide includes both cognitive and affective development, while Junior High schools only focus on cognitive development. Also, teachers at Middle schools teach several disciplines while Junior High schools have teachers dedicated to specific subjects. Junior Highs have a more traditional approach to education and their curriculum focuses on academic subjects, while Middle schools are more experiential with exploratory and non-academic classes in addition to the usual academic ones. Moreover, Middle school classrooms are set-up for close proximity whereas junior high classrooms follow a traditional high school type set-up.
At 14, students go on to High School or Senior High School. High schools can be subdivided into different types of schools: Vocational Schools, Magnet Schools, College Preparatory High School (Prep-Schools) or Special High Schools.
- Vocational High Schools: For students who already have an idea of their future professional career. They offer hands-on training to prepare students for a particular field. Students are prepared for direct entry to the industry at the end of their studies at a vocational (or technical) high school, or if they wish, they can pursue their studies in a post-graduate vocational or technical institution.
- Magnet Schools: These schools focus on one or several subjects, from science, to mathematics, to fine arts. Entrance requirements vary according to the school and may include a competitive entry exam or even be based on a random draw.
- College Preparatory High Schools: Specially designed schools for advanced students with strict entry requirements. The courses offered are all classified as honors, International Baccalaureate, or Advanced Placement.
- Special High Schools: Special High Schools are designed for students with disciplinary or mental health issues that make it hard for them to study in a traditional general high school.
Once students have entered high school, they start 9th Grade, or what is referred to as "Freshman Year". High school courses include English, mathematics, science and social science, foreign languages, and physical education. Optional courses are also available such as music, art or theatre. In addition, many high schools offer vocational training courses. High school ends with 12th Grade, "Senior Year", when students are 18 and leads to a High School Diploma.The majority of students finish high school but, depending on the State, students may only be required to attend school until 16, 17 or 18.
Preparation for University in High School
Advancement Placement Program:
The Advancement Placement Program provides college level courses at high schools, in the US and Canada. It is linked to the first year of a university undergraduate program and can give students academic credits toward the first year of their university studies. The AP (Advancement Placement) exam aims at providing universities with information about a student's knowledge in a particular subject, and their skills and academic abilities, to decide whether or not to grant them credit.
POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION
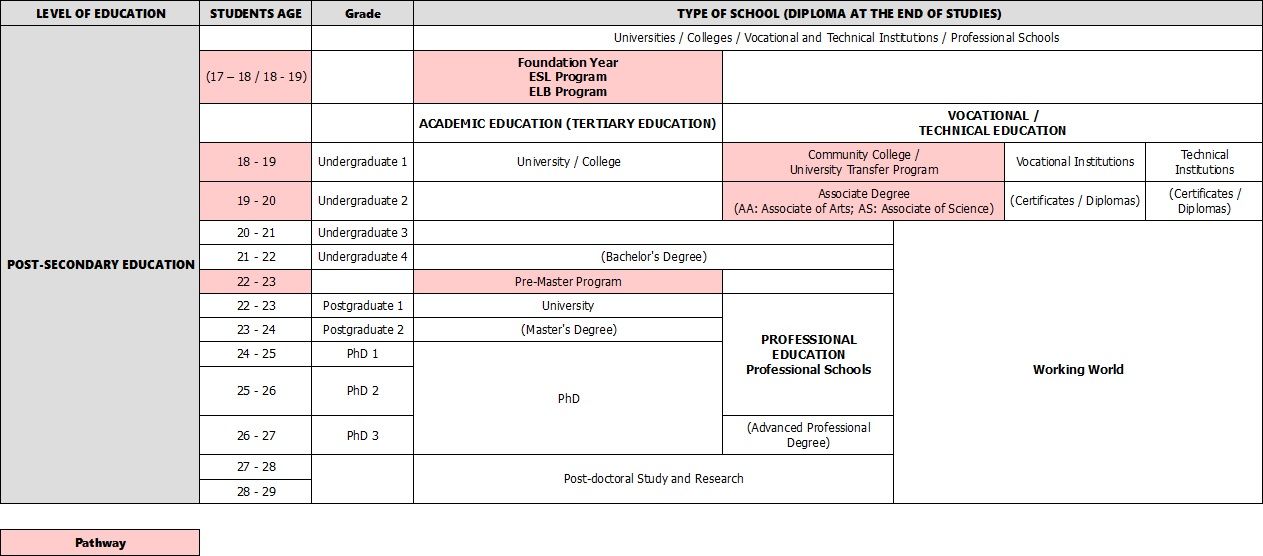
After high school graduation, students can choose to continue their studies at a post-secondary institution. Different types of education are available within this category:
- Academic or Tertiary Education at an American university or college after High School
- Vocational/ Technical Education at vocational and technical institutions, as well as community colleges after High School.
- Professional Education at professional schools after having completed an undergraduate program (Bachelor's Degree)
Tertiary Education = Academic Education at University
If students choose to follow an academic or tertiary education, they have two options: enter a college or a university. In general, colleges are smaller than universities, and only offer undergraduate programs (Bachelor's Degree), whereas universities allow students to pursue their studies through post-graduate programs (Master's Degree and Ph.D.). However, the academic level of the undergraduate program at both types of institution are equal.
University Requirements:
In order to enter a university in the US, students need to meet criteria. Universities will look at:
- their high school course of study
- their high school Grade Point Average**(GPA)
- their participation in extracurricular activities
- their SAT (Scholastic Aptitude Test) or ACT (American College Testing) exam scores
- a written essay
- possibly a personal interview
**Grade Point Average: The student's High school Grade Point Average is a figure showing the student's average grade throughout his or her high school studies. In the American educational system, students are graded with letters, from A (best grade) to F (worst grade). Each letter corresponds to a certain amount of points: A+/A = 4 points; A- = 3.7; B+ = 3.3, B = 3; B- = 2.7; C+ = 2.3; C = 2; C- = 1.7; D+ = 1.3; D = 1 point and E/F = 0 point. The grades, or more precisely the points received for each course during high school are added, then divided by the total number of courses to get the average grade. The final number is the student's GPA.
The student's participation in extracurricular activities, such as art clubs, theatre, or athletic teams, proves that the student acquired teamwork and leadership skills that will be great advantages for his or her further studies in a university.
Students need to take the SAT or the ACT in order to enter universities in the US. The SAT (Scholastic Aptitude Test) is one of the admission tests, along with the ACT, required by American Universities. Most students take it during their last year of high school. Each university has its own required SAT or ACT score. The SAT lasts 3 hours 45 minutes and is divided into three sections: Critical Reading, Maths and Writing. It aims at analysing students' critical thinking and analytical skills. The ACT (American College Testing) focuses on English, mathematics, reading and science reasoning. In addition, students can take an optional writing test.
The essay length and content depend on the university to which students apply.
Some universities may require a personal interview with a representative of the admissions board to have a better understanding of the student's level and ability to pursue academic courses.
In order to reach the academic and English level required by universities in the US, foreign students can follow pre-undergraduate, undergraduate and postgraduate preparatory programs.
International Baccalaureate Programme (IBP):
This program is for international students between age 16 and 18 who want to enter one of the more prestigious universities in the US or other English-speaking countries. At the end of the program, students take a series of 6 exams and are granted an IB Diploma. This program is recognised in 50 countries and allows students to enroll straight into the second year of an undergraduate program at American universities.
There are two types of undergraduate pathways in the US: academic pathways, in which students study both academic subjects and the English language, and pathways primarily focusing on English language studies, with some academic subjects studied in addition.
- 1. Academic Undergraduate Pathways:
The most famous undergraduate pathway program is the Foundation Program, also called by some institutions "Foundation Year Program", "Undergraduate Pathway Program", or "Year Zero". Students can follow this 1-academic year program after high school graduation and later enter the second year of a Bachelor's Degree program at university.
- 2. English Language Pathways:
Besides academic pathways, there are programs specifically designed to prepare students for the English level requirements of universities, such as the ESL Program (English as a Second Language program) and the ELB (English Language Bridge).
Bachelor's Degree (Undergraduate Program):
Once students have successfully passed all the tests and exams required by the universities and they have finally enrolled in one, they start an undergraduate program, a 4-year program to obtain a Bachelor's Degree. Most American universities offer a liberal education. Meaning that students have to take courses across several academic subjects to ensure a broader academic knowledge before specializing in one specific field of study called "Major". Courses are generally one semester long and are given a number of credit hours (points), generally 3, according to the number of hours per week spent in class. Before graduation, that is, before students receive their Bachelor's Degree, they must have gained a certain amount of credits. Usually, students do not need to write a thesis for their Bachelor's Degree.
Pre-Master Program:
Students who want to pursue their studies after their Bachelor's Degree can prepare for their Master's Degree via a Graduate Pathway program known as a Pre-Master Program. This program aims at preparing students for the demands of a Master's Degree program at a university, on both an academic level and in terms of English proficiency. It also allows students who want to change their major after completing a Bachelor's Degree, to acquire the necessary knowledge in their new field of study before beginning their Master's Degree program. It is also very useful for foreign students, to familiarize them with American culture and environment and provide academic credits toward their upcoming Degree.
Master's Degree (Postgraduate Program):
After graduation, students can decide to deepen their knowledge in their field of study by continuing their education through a Master's Degree. This is a 2-year program. Students wishing to take such a program must meet requirements such as:
- Completion of a Bachelor's Degree
- Competitive GPA
- Write an essay or send a writing sample
- Minimum GRE (Graduate Record Examination) score
The GRE (Graduate Record Examination) is a test focusing on verbal and quantitative reasoning, critical thinking, as well as the student's analytical writing ability.
Contrary to the Bachelor's Degree, most of the Master's Degree required to write a thesis. Masters include fields such as Business, Engineering, or Education. An MBA, Master of Business Administration, is a type of Master that focuses on general management, putting forward business skills like human resources or accounting.
PhD (Doctor of Philosophy degree or Doctorate of Philosophy) (Postgraduate Program):
After a Master's Degree, students may want to pursue their academic studies until the end of their education. In that case, they enter in a 3-year program in order to get a PhD, a Doctor of Philosophy degree, also called a Doctorate of Philosophy. Students will attend courses until they attain the number of credits required to take their qualifying exams. Those exams generally last several days and include both a written and an oral part. After their exams, students start writing their dissertation which they will have to defend in front of the faculty committee before being awarded their Degree. Each university and department will have its own specific requirements at this level.
Post-Secondary Vocational/Technical Education
Vocational Institutions:
Post-Secondary Vocational Institutions are where graduates of Vocational High Schools can continue their studies. It aims at preparing students for the job market in a particular occupational field at a higher level than the one reached during secondary education. The most popular discipline taken by students in vocational institutions is business, but possible subjects are as varied as in secondary education, including careers in health, trade and industry.
Technical Institutions:
In the same spirit as vocational institutions, technical institutions focus on giving students a specialized training to turn them into experts in a particular subject. Technical institutions focus more on computers and data processing, engineering, science and communication technologies or protective services.
Both vocational and technical institutions offer 2-year programs ending in a specialized Certificate or Diploma.
Community Colleges:
Students enter a Community college after high school graduation and having completed 12 years of elementary and secondary education. Community College, also named "Junior College", is a 2-year program to help prepare students for the academic style teaching typical at universities and to give them a strong foundation knowledge before focusing on one particular subject. At the end of the 2 years, students can both get an Associate Degree (A.A.: Associate of Arts, A.S.: Associate of Science). With this degree students can transfer into the third year of an undergraduate program at a university (University Transfer Program), or enter the workforce. Students often choose to follow this path because admission to a Community College is easier than to a university, tuition costs are lower, and the class size is generally smaller than at a university.
Professional Education
Professional education is provided by professional schools in subjects like Medicine, Theology, Law, Business and so on. This is why professional schools can also have the name of Medical school, Law school or Business school. Programs last from 1 to 5 years, depending on the field of study and are taken after having completed an undergraduate program (a Bachelor's Degree). They lead to a Professional Degree. For example, programs at Law schools run for 3 years and lead to a Doctor of Juridical Science (J.S.D or S.J.D), while those at medical schools are four years long and end with the obtention of a Doctor of Medicine (M.D) or a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) Degree.