EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM IN THE UK
PRIMARY EDUCATION
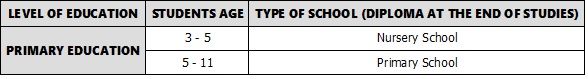
The British educational system is designed for students aged 3 and up, and can continue to approximately 26-27 years of age, in cases where students complete a PhD, the last level of education in the United Kingdom.
From 3 to 5 years of age, British pupils go to Nursery school. It is their first experience with the British educational system, but is not mandatory. Students can skip this and go directly to Primary school at age 5 and until they are 11 years old. Primary School Education is compulsory.
SECONDARY EDUCATION
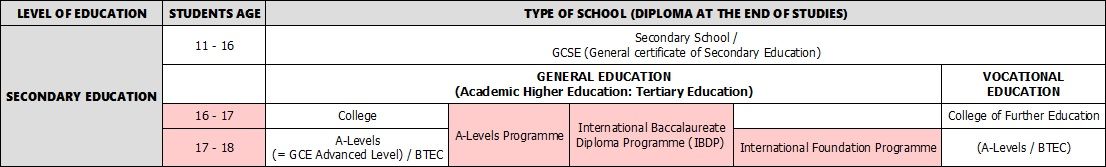
After having completed Primary school, British students must enroll in a secondary school where they will study until age 16. They then take a final exam, the General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE), which is meant to assess their level at the end of their secondary school studies.
After passing the exam, British students complete their secondary education by enrolling in a college. At this point, at 16 years of age, students choose between 2 possible options: general or vocational education.
General Education, also called "Academic Higher Education", is designed for students intending to further continue their studies in academic programmes at university. Students in General education will prepare for their A-levels. Exams which will allow them access to further education at a University level.
Vocational Education, also called "Vocational Further Education", is designed for students who have already decided on a future professional career which is more technical or technological.
POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION
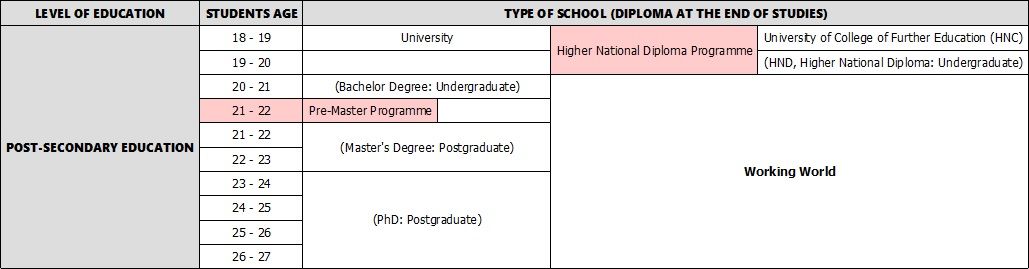
Once students have completed their two years of college, in general or vocational education, they begin their post-secondary education at either a general education university or a vocational university or college.
Pathway Programmes between College and University in General Education
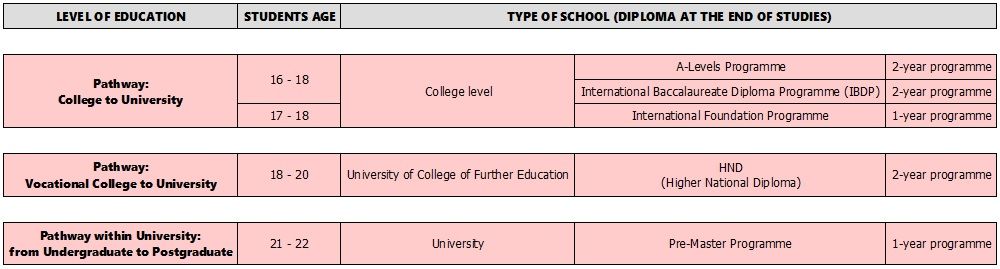
Entering University in General Education (Academic Higher Education=Tertiary Education))
In order to continue their studies at a general education university in the UK, a Certificate of Secondary Education (CSE), such as the A-Levels* (GCE Advanced Level) or the IB** (International Baccalaureate), is mandatory. The CSE attests to the student's level of English and their proficiency in academic skills, proving that they have attained the levels expected by British universities.
*A-Levels: A-Levels, also called A-Level Diploma or GCE Advanced Level, is the final certificate students receive upon completion of their secondary studies, when they are about 18 years old. It This qualification is needed to gain admission to a British university, although some equivalent diplomas are also accepted, such as the International Baccalaureate (IB).
The A-Levels exam is the standard qualification and the most common method used to ascertain a student's eligibility for a degree programme at a university in the United Kingdom. The test is internationally recognized and proves that the student has a knowledge of English sufficient to attend courses at a British university.The A-Level can be studied in secondary school in the UK, or in national or international colleges. International colleges are more suitable to foreign students. Students can freely choose the subjects they wish to study, but need to have a clear idea of their future career.
**IB (International Baccalaureate): The IB is an international preparatory programme recognized by many of the world's leading universities such as Cambridge or Oxford in the UK, or Harvard, Yale and Princeton in the US. The choice of subjects is more reduced than what is available for the A-Levels, however the programme in itself offers a broader education.
Pathways to a General Education University
Foreign students who want to enroll in British universities need to have certification equivalent to the Certificate of Secondary Education. Students must take a compulsory preparatory programme. This type of programme is called a "Pathway Programme" since it is a "path" between college and university. Pathways leading from a general education college certification to university prepare foreign students to reach both the academic and English language levels required by British universities. It is not a bridge between two different kinds of education, but a preparation for entry to a university. There are 3 possible Pathway Programmes to follow in order to gain admission to general education universities in the United Kingdom:
- 1. International Foundation Programme
- 2. A-Levels Programme
- 3. International Baccalaureate Programme (IBP)
In order to enroll at Oxford or Cambridge University or at any Faculty of Medicine in the United Kingdom, it is mandatory to have completed either the A-Levels Programme or the IB Programme.
- 1. International Foundation Programme (also known as "International Foundation Year", "University Preparation Year Programme" or "Foundation Year Programme", or "Preparatory Programme Foundation"):
The programme, from 6 months to a year, ensures that students acquire the knowledge of a specific field of study equal to that of the first year of an undergraduate university programme and brings the student's level of English to a par with that required by UK universities. It bridges the gap between a student's current qualifications and university requirements. This programme is available at specialist private or public colleges, as well as at the universities themselves, often where the student plans to study in the future. In those case it also serves to familiarise students with the British way of life, the campus environment and UK culture.
More information about the International Foundation Programme - 2. A-Levels Programme (Advanced Levels):
This programme prepares students for the A-Level exam. The better the result of the exam, the more chances students have to enter the British university of their choice. The A-Level, or the IB Programme, is mandatory to enter top universities such as Oxford or Cambridge.
More information about the A-Levels Programme - 3. International Baccalaureate Programme (IBP):
This programme prepares students for a particular course of study at university. At the end of the programme, students take a series of 6 exams to obtain the IB Diploma. For each exam, students are given points, from 1 (the lowest) to 7 (the highest). The maximum total score is 45. Students can gain an additional 3 points with the thesis they write and their CAS participation, in addition to the 6 subjects studied. Students must receive a minimum of 24 points in order to get the IB Diploma. For admission to the more prestigious universities of the world, students should have a minimum of 35-36 points.
More information about the International Baccalaureate Programme
Undergraduate Studies
To be eligible for an undergraduate programme at a university in the United Kingdom, students must meet certain requirements:
- Minimum age: 17.5 years
- Completion of 12 years of Primary/Secondary education
- Minimum IELTS score of 5.5-6.0
Most courses are taught in universities, but many are taught at colleges, specialist art institutions, business schools and agricultural colleges.
Types of Undergraduate Studies in General and Vocational Education:
Bachelor's Degree: This is a three year programme offering students a deep understanding of a particular academic subject. Students can specialise in different areas and obtain different types of Bachelor Degrees at the end of their studies, such as: Bachelor of Arts (BA); Bachelor of Education (BEd); Bachelor of Engineering (BEng); or a Bachelor of Science (BSc).
Degrees can be classified as "Ordinary" or "Honours". Usually, a Degree is "Ordinary" or "Unclassified" when students have completed the Degree programme without achieving the grades required for an "Honours" Degree.
Foundation Degree: This is the equivalent of the first 2 years of an Honours Degree. It can be either a part- or a full-time programme and combines academic studies with work-based, practical learning with a certified employer.
Diploma of Higher Education (DipHE): This programme is the equivalent to the first 2 years of a Bachelor's Degree and can be a path to the third year of a related degree. It can include some academic courses, but they are generally provided by vocational universities or colleges allowing students to specialize in a field linked to their future profession, like social work, for instance.
Certificate of Higher Education (CertHE): This programme focuses either on a specific job, or on academic studies. It is the equivalent to the first year of a Honours Degree and is the most basic level of undergraduate education. It testifies to the student's ability to follow courses at university. Students attend this programme to make find out if they will be happy in a higher academic environment and able to keep pace. They can then change careers, or continue on to a Foundation Degree, a Diploma of Higher Education or a full Honours Degree.
Higher National Diploma (HND): This course, available at vocational colleges or universities, lasts 2 years and can be a bridge to general education (academic higher education) and the third year of a Degree in a general education university. Students first study in a vocational college or vocational university to deepen their knowledge in a specific field before transferring to a general education university to finish their degree. In other words, they start their tertiary education in a vocational college, and finish their studies in a general university after 2 years of vocational college.
More information about the HND
Postgraduate studies
Postgraduate studies logically follow undergraduate studies. Usually, students need to have completed an Undergraduate Degree to enter such a program. After their Bachelor's Degree, students can chose to do a Master's Degree and then further pursue their studies with a PhD.
In General Education
Pre-Master Programme:
Students wishing to do a Master's Degree after their Bachelor's Degree can prepare for their postgraduate studies through a Pre-Master programme or course, also called "Postgraduate Foundation course". This programme aims at giving international students the English knowledge and academic skills required for successful completion of a Master's Degree at university. It also familiarises students with the British way of teaching at a Master's level.
More information about the Pre-Master Programme
Master's Degree: The next step after a Bachelor's Degree. Lasting 2 years, it deepens the knowledge acquired during the Bachelor's Degree. There are two types of Masters: taught and research. The taught Masters are programmes involving lectures and seminars. Students are evaluated through coursework and exams. The research Masters are more in-depth programmes focusing on one subject in particular about which students need to write a thesis or a dissertation.
Most Master's courses lead to a Degree named MA (Master of Arts) or MSc (Master of Science). However, there are other qualifications for other specialised subjects such as MEng (Master of Engineering), MFA (Master of Fine Arts), MArch (Master of Architecture), LLM (Master of Laws), MPhil (Master of Philosophy)... The MPhil tends to be more research-oriented and generally taken by students to continue their studies afterwards with a PhD.
MBA courses (Master of Business Administration): An MBA is internationally recognised and gives students the skills they need to start a management career. The programme includes subjects such as business policy and strategy, market research, marketing, operational and strategic management, leadership, entrepreneurship, finance, accounting, IT, human resource management and international trade.
PhD/DPhil (Doctor of Philosophy or doctorate): This is the highest academic level that students can reach. This Degree often leads to a career in academia, such as a university professor, lecturer or researcher. Even though a Master's Degree is not compulsory to take a PhD, the majority of the students first attend a Master's Programme before applying for a PhD. The successful completion of a PhD usually takes 3 to 4 years.
In Vocational Education
Conversion Courses: This course is delivered by vocational colleges to allow students to change their subject area after their undergraduate studies and to be more prepared to enter the working world.