EDUCATIONAL SYSTEM IN AUSTRALIA
EARLY CHILDHOOD EDUCATION

Before primary school, childcare services are available for babies and children aged 0 to 4, and even up to 6 years of age. Childcare services can be provided by public institutions, such as government agencies or community groups, but many parents also opt for private providers like nannies or babysitters. Parents have the option to put their children in preschool, also called kindergarten, when their children reach the age of 4.
PRIMARY/ELEMENTARY EDUCATION
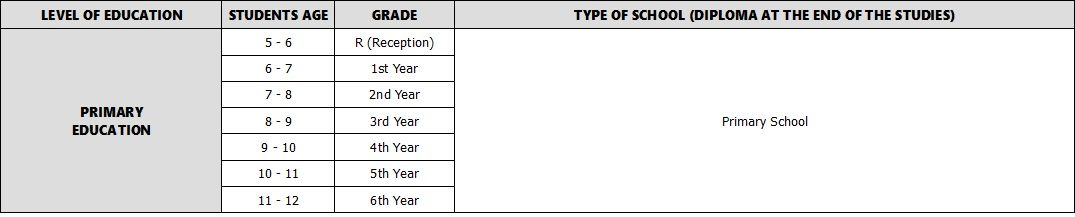
At 5 years of age, children have the possibility to enter a Primary school through a "Reception" year to acclimatize themselves to the school environment. However, the official first year of primary school, and thus primary education, is at age 6. From that point, school is mandatory for all Australian children until they reach 17 years of age. Government-run primary schools are also often called public primary schools. Some public primary schools are located at the same place as high schools and are then called R-12 schools (Reception to Year 12), area schools (public schools in rural areas) or colleges.
During their primary years, students will start with English classes, focusing on reading and writing, mathematics, and the Study of Society and the Environment (SOSE). In addition, students have other courses such as science, computer studies, music, sports and drama. They also can participate in extracurricular activities like choir, chess or orchestra.
Primary school can last until Year 6 or 7 depending on the school. Students then are 12 or 13 years old and are ready to enter secondary education.
SECONDARY EDUCATION
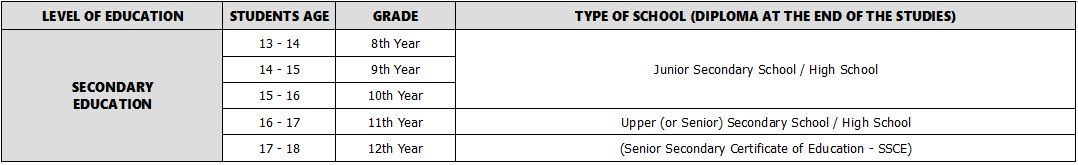
Students start their secondary education in a either a junior secondary school or a high school. Junior secondary school lasts 3 years (if started in Year 8) or 4 years (if started in Year 7) and is then followed by 2 years of senior secondary school. Students can also attend a high school which combines both junior and senior secondary schools and lasts 5 or 6 years.
During Year 11 and Year 12, the last two years of upper (or senior) secondary school/ high school, students prepare for the Senior Secondary Certificate of Education (SSCE) which they will obtain at the end of their secondary education. Each student is ranked according to a nationally standardised final score on the SSCE, called the Australian Tertiary Admission Rank. Universities usually use this ranking to evaluate an applicant's academic level. This certificate, the SSCE, is only granted to domestic students. International students can prove equivalent qualifications for application to Australian universities through the "International Baccalaureate" (IB) or the "Accelerated Christian Education" (ACE), which are both certificates attesting that students have reached the same level as the Year 12 of secondary education in Australia. While the IB is well accepted by Australian universities, applicants with an ACE may need to provide additional proof with the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT).
Check the pathway to prepare for the International Baccalaureate.
At the end of their secondary education, when students have completed 12 years of education and reached the age of 18, they can choose between following an academic higher education or a vocational education and training (VET).
POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION
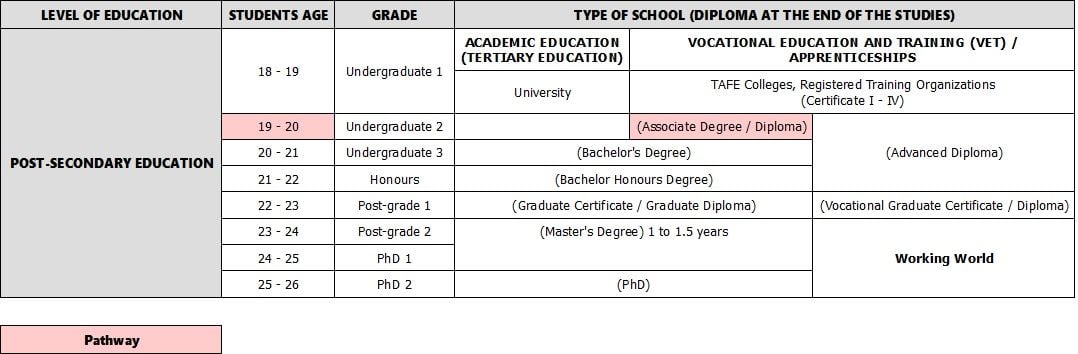
Academic Higher Education
Australia, contrary to some other countries like the United States, does not rank its universities but the latter are classified according to the type of courses they provide. Some of them put forward research studies according to the region where they are located: universities in rural areas are likely to specialise in subjects such as agriculture or ecology, and universities in a tropical region might offer a tropical medicine programme, for instance. Some universities, contrary to the ones that only focus on academic subjects with a very theoretical approach, offer more practical courses with case studies and other real-life exercises to better prepare students for their future jobs.
University Entry Requirements:
If students choose to enter an Australian university directly after their secondary education, they must provide specific proof of their academic skills:
- having completed their secondary education, with the obtention of their Senior Secondary Certificate of Education (SSCE)
- a minimum IELTS score of 6.0 or higher
- specific requirements according to the university, such as interviews or additional papers
Pathway to University for International Students: Foundation Studies Program (1 year)/ Fast-Track Program (9 months):
Foreign students wishing to enter an Australian university can attend a Foundation Studies Program, also called "Preparatory Foundation Program". This program usually lasts 1 year, or 9 months (30 to 36 weeks) for fast learners with a high level of English and academic skills. It is designed for non-native English speaking students who want to enter the first year of an undergraduate program in an Australian university. It helps students to adapt to the academic environment and day-to-day life in Australia by preparing them to meet the academic and English knowledge requirements for entry to an undergraduate program at universities and colleges in Australia.
Bachelor's Degree:
A Bachelor's Degree is the first step in higher academic education. This university program lasts 3 years, but students can extend it to 4 years by taking an "Honour" year. Usually, students take a double Bachelor program or combine two Bachelor's Degree programs to get two Bachelor's Degrees, especially in general subjects such as Art, Business, Law and Science. Universities however offer a large variety of disciplines, from Engineering to Health Sciences, to Humanities, to Management.
Honours Degree:
At some Australian universities, if a student obtains a high grade average during their three years of undergraduate studies, they can apply for an Honours Degree. A Bachelor Honours Degree is a means to deepen one's knowledge of one's chosen field through research. It is obtained after an additional one or two years of study consisting of higher level courses and upon completion of a research thesis. It is a step between undergraduate and postgraduate studies but is not necessary in order to apply to a master's degree, in fact, in some cases where very high grades are obtained, it may be possible to apply directly for a doctoral program without first completing a Master's.
Pre-Master Program:
This program allows students to be ready to start a Master's Degree by providing English courses and academic lectures and modules in the field of study of the student's choice. It can last 6 or 9 months according to the student's learning ability.
More information about the Pre-Master Program
Master's Degree:
After having completed a Bachelor's Degree, students can decide to deepen their knowledge in their chosen field at a postgraduate level with a Master's Degree. This program generally lasts 1 to 2 years and enables students to be better recognised by employers in the working world. Masters are available in many disciplines, as the Bachelor's Degree: Creative Arts, Business, Education, Engineering, Health, Sciences... There are two different types of Master providing two different kinds of courses: taught courses, that are traditional courses, and research courses, focusing on independent research. Students can combine both types if they want to.
Students usually need to have completed a Bachelor's Degree with above average grades to apply for a Master's program.
Doctorate Degree (PhD):
A Doctorate Degree in Australia can last 2 to 3 years. It is the highest academic level of education and is available in several disciplines: Doctorate of Philosophy (Ph.D), Doctorate of Medicine (M.D), Doctorate of Dental Surgery (D.D.S), Doctorate of Physical Therapy (D.P.T), ...
Vocational Education and Training (VET)
VET Institutions:
If students choose a vocational path, they will have more practical classes in order to be prepared for the working world or further education and training. Those courses are delivered by public or private training institutions. Private training institutions are also more generally called "Registered Training Organizations" (RTOs). Government-funded, public training institutions are known as colleges, community education centres, and TAFE (Technical And Further Education) colleges.
VET Requirements:
In order to enter a VET institute, students need to meet certain requirements:
- completion of their secondary education and obtention of a Senior Secondary Certificate of Education (SSCE) or equivalent
- provide a copy of their secondary school/ high school transcript
- a minimum IELTS score of 5.5, for most of the institutes
Certificates and Diplomas:
Public and private VET institutions offer from Certificate I to Advanced Diploma. More and more also offer Bachelor's Degree programs, and a few of them provide Master's Degree programs as well.
- Certificates I-II-III-IV:
Certificate I and II provide basic vocational knowledge and introduce students to general and more specific subjects related to the working world like Business or Information Technology. Certificate III and IV deepen the student's knowledge and skills in very specific fields of study, according to the student professional plan, such as Computer Graphics or the Music Industry. It takes 6 months to 1 year to get those certificates.
- Diploma:
The Diploma gives students an advanced and technical knowledge in a specific field and needs 2 years to be achieved.
- Advanced Diploma and Associate Degree:
Students need to study 2 to 3 years before getting an Advanced Diploma or Associate Degree. They are equivalent to the first 3 to 4 semesters of a Bachelor's Degree program. Advanced Diploma is delivered to students wishing to continue on a vocational path, while the Associate Degree is for students who want to move into the academic realm.
- Vocational Graduate Certificate/ Diploma:
The Vocational Graduate Certificate and Diploma offer high-level skills and knowledge for paraprofessional careers. The Vocational Graduate Certificate takes 6 months to 1 year to fulfill, while the Vocational Graduate Diploma need 1 to 2 years to be completed.
Pathway from VET to Higher Education:
Students having completed a Diploma or Associate Degree in a TAFE college or RTO can get credits in order to directly enter the second year of an undergraduate program in a university. The number of credits granted depends on the content of the vocational courses and the number of places available in the undergraduate program for instance. Some vocational training institutions have partnerships with universities which guarantees students a place at the university. Starting off with vocational education training and later transferring to an academic program at a university can be a great option for many students since they can enter a university with a lower level of English and less strict academic pre-requisites than those required for university entry directly after secondary education. At a vocational institution, international students who speak English as a second language are able to reinforce their language skills and interact with native English speakers before entering an Australian university.
LANGUAGE COURSES
Foreign Language Courses
Many schools in Australia offer bilingual programs or programs in another language.
English Language Courses
Beginning at a Senior High level and even up to the Doctorate Degree or PhD level, students can take English courses to ensure that their level is on a par with the language level required by high schools and universities in Australia. They can attend the following English language programs:
- General English
- English for Academic Purposes (EAP)
- IELTS Preparation
- English for TESOL (Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages)
- English for High school preparation
English for Academic Purposes (EAP):
This program aims at getting students to the level of English required to continue their studies at a university or vocational institution. It can last from 1 to 6 months (4 to 24 weeks) and combines listening, vocabulary and grammar, planning and writing reports, academic papers, in-class presentations and discussions, team projects, and advice on how to sit formal exams.
More information about EAP
IELTS Preparation:
In Australia, many educational institutions only accept the IELTS as a proof of a student's level of English.
The majority of English schools in Australia provide preparation courses to the IELTS exam and some of them are also IELTS testing centers.
English for TESOL (Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages):
This program is created to prepare teachers as well as researchers and other future academic professionals to teach in English as a second language. It gives them the language, literacy and linguistic ability and communication foundations to teach non-native English speakers.
English for High School Preparation:
This is an intensive English program to prepare students for the level of English expected in a high school setting. It includes learning the typical vocabulary used for high school subjects and acquiring the communication skills they will need to make themselves understood.